Joseph Coffland
jcofflan@users.sourceforge.net
April 5, 2006
Copyright ©2004, University of Amsterdam. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included with this documentation, GNU Free Documentation License.
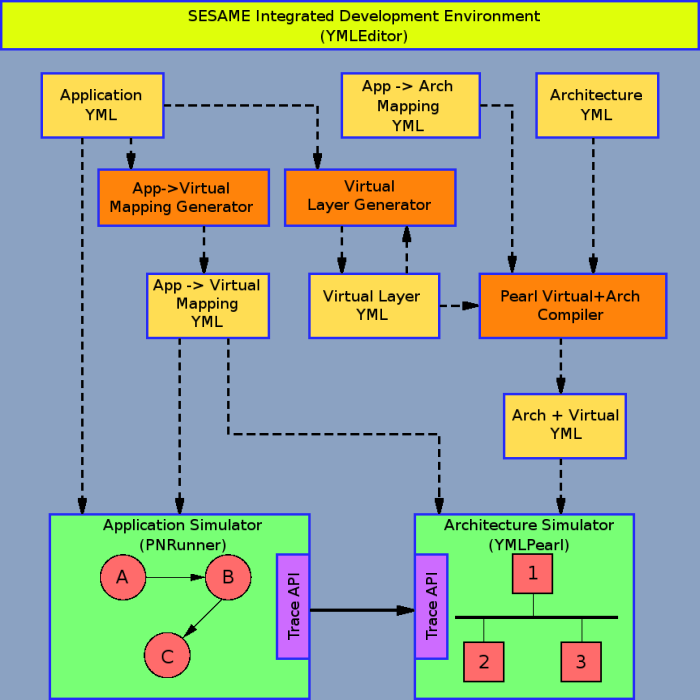
SESAME is a project at the University of Amsterdam which stands for Simulation of Embedded Systems Architectures for Multi-level Exploration. SESAME employs event driven cosimulation to simulate embedded systems. SESAME follows the Y-Chart methodology for embedded system design. Y-Chart recognizes distinct application, architecture and mapping layers within an embedded system simulation. Unlike standard cosimulations applications in SESAME are simulated separately from their architectures. This separation provides several benefits including reuse of application models with different architectures and the ability to optimize an architecture for more than one application.
SESAME uses Kahn Process Networks (KPN) for application simulation. KPNs expose the parallelism and communication behavior of an application. They also guarantee deterministic, deadlock free execution. As an application simulation is run it generates event traces which describe the applications behavior. The KPN application simulator used in SESAME is called PNRunner or Process Network Runner.
These event traces are mapped on to an architecture simulation via the virtual layer. The virtual layer has also been referred to as the synchronization layer because it synchronizes trace events from different application processes according their mapping on to the architecture model. However, it is also responsible for event scheduling and trace reordering.
SESAME uses an discreet event simulator called pearl to simulate both the architecture and the mapping layer. Architecture simulations respond to application events they receive via the mapping layer by simulating their timing consequences.
When the simulation is finished the user can analyze the measured simulation results and use this information to improve or refine the application simulation, the architecture simulation, the mapping or all three. Thus, the user runs through iterations of simulating and refining the simulation model until satisfied with the embedded system's performance.
The remainder of this document describes the structure of the SESAME software and provides information on how the software system works as a whole. Documents which describe how to use the individual parts of the software system are referenced.
You may already have gcc 3.2.2 or better, the GNU build tools and perl installed on your system. Follow the instructions on the website for installing Xerces C++.
tar xzvf sesame-builder-x.x.x.tar.gz
This will create the directory sesame-builder-x.x.x. Change to this directory.
export XERCESCROOT=/usr/local export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
./configure --prefix=<directory>
Note: You cannot easily change this directory later with out rebuilding everything.
make
If the packages do not build correctly, try to fix the problem and rerun make. The script will continue where it left off.
If the build was successful then SESAME should be properly install in configured installation directory.
Additionally, for auto-routing to work which is necessary to view unrouted graphs properly you must have dot, a graph routing program which is part of ATT's GraphViz software, installed and on your PATH.
Now run ./ymleditor.
Alternatively, you can open the MJPEG example from the comand line by running ./ymleditor examples/mjpeg/mjpeg.yml from the ymleditor directory. Run ./ymleditor help for more information about the YMLEditor's command line options.
Clicking on a box in the image below will bring you to the documentation for that software component.

| PNRunner(1) | Application Simulator |
| ymlpearl(1) | Architecture Simulator |
| ymlpearlexec(1) | Architecture Simulation Executable |
| ymlpp(1) | YML preprocessor |
| SESAMERunner(1) | SESAME Cosimulation Runner |
| AppVirtualMapGenerator(1) | YML Processor |
| ArchitectureCompiler(1) | YML Processor |
| VirtualLayerGenerator(1) | YML Processor |
| PNRunnerYMLTool(1) | PNRunner YML Tool |
| PearlYMLTool(1) | Pearl YML Tool |